Key Differences Between IT and Computer Information Systems: A Comprehensive Analysis
Exploring the distinctive features of IT and Computer Information Systems unveils a fascinating comparison that sheds light on their unique roles and applications in the tech industry. As we delve into the key disparities between these two fields, a clearer understanding emerges, offering valuable insights for those navigating career choices or seeking to broaden their knowledge of technology domains.
Delving deeper into the realm of IT and Computer Information Systems, we uncover a plethora of differences that shape their educational paths, career trajectories, and impact on businesses.
Key Concepts

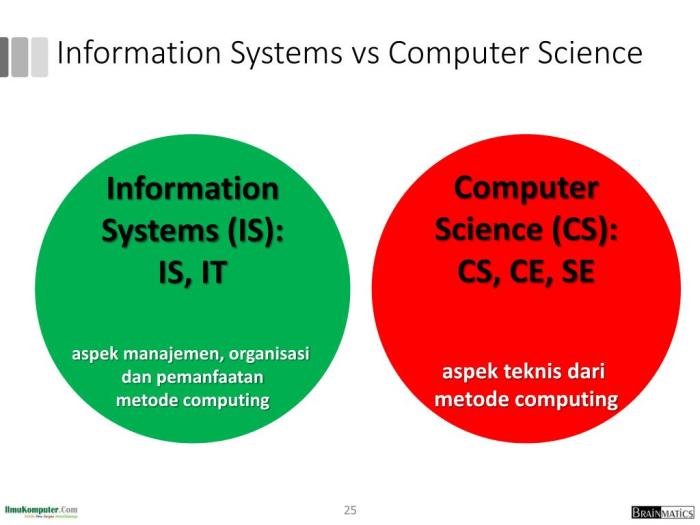
IT (Information Technology) and Computer Information Systems are two closely related fields in the realm of technology. IT refers to the use of technology to manage and process information, typically involving the use of computers and software. It encompasses a wide range of activities such as hardware and software development, networking, cybersecurity, and data management.On the other hand, Computer Information Systems focus more on the application of technology in business settings.
It involves the use of technology to solve business problems, improve efficiency, and support decision-making processes within an organization.
Differences in Focus and Scope
- IT focuses on technology infrastructure and systems management, ensuring that hardware and software components work together seamlessly to support organizational needs.
- Computer Information Systems, on the other hand, focuses on the strategic implementation of technology to meet business objectives and improve overall operations.
Examples of Applications
- IT applications include network administration, cybersecurity, database management, software development, and technical support services.
- Computer Information Systems applications involve the use of technology for customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), business intelligence, and decision support systems.
Education and Skills
When it comes to pursuing a career in IT or Computer Information Systems, there are distinct educational requirements and technical skills that differentiate the two fields.
Educational Requirements
In general, a career in IT typically requires a bachelor's degree in information technology, computer science, or a related field. On the other hand, Computer Information Systems professionals often hold a degree in information systems, business administration with a focus on information systems, or a similar field.
While both fields may have some overlap in coursework, the emphasis in each program can vary based on the specific industry needs.
Technical Skills
IT professionals are expected to have strong technical skills related to networking, cybersecurity, systems administration, and programming. They often need to stay updated on the latest technology trends and tools to effectively manage and troubleshoot IT systems. On the other hand, Computer Information Systems professionals focus more on the application of technology in a business setting, requiring skills in database management, system analysis, project management, and information security.
Curriculum Differences
The curriculum for IT programs typically includes courses on programming languages, network administration, cybersecurity, and hardware/software management. In contrast, Computer Information Systems programs may offer courses on database design, business intelligence, project management, and information systems analysis. The goal of each program is to prepare students for different career paths within the broader field of technology, with IT focusing more on technical implementation and support, and Computer Information Systems focusing on the strategic use of technology in a business context.
Career Paths
When it comes to career paths in the IT industry, there is a wide range of opportunities available for professionals with diverse skill sets and interests. From cybersecurity specialists to network administrators, software developers to IT project managers, the field offers a plethora of roles to explore.
On the other hand, Computer Information Systems professionals typically work in roles that involve managing and utilizing technology to solve business problems. These roles can include systems analysts, database administrators, IT consultants, and more. Their responsibilities often revolve around optimizing technology systems to meet the needs of organizations.
Job Roles and Responsibilities
Within the IT industry, job roles can vary significantly depending on the specialization. For example, a cybersecurity analyst is responsible for protecting an organization's data and systems from cyber threats, while a software developer focuses on creating and maintaining software applications.
IT project managers oversee the planning, execution, and completion of IT projects.
In Computer Information Systems, professionals are tasked with analyzing and implementing technology solutions to improve business processes
Job Prospects and Growth Opportunities
- IT professionals often enjoy a high demand for their skills, with job prospects expected to grow as technology continues to advance. Specialized roles such as data scientists and cloud architects are particularly in demand.
- Computer Information Systems professionals also have promising job prospects, especially as businesses increasingly rely on technology to drive their operations. Roles like business intelligence analysts and IT project managers are projected to see growth.
- While both fields offer opportunities for career advancement and high earning potential, IT professionals may have more diverse options due to the constantly evolving nature of technology.
Technologies and Tools
In the ever-evolving field of IT and Computer Information Systems, professionals rely on a variety of technologies and tools to carry out their tasks efficiently.
Common Technologies and Tools in IT Roles
- Operating Systems (e.g., Windows, macOS, Linux)
- Networking equipment (routers, switches)
- Cloud computing platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
- Programming languages (Java, Python, C++)
- Virtualization software (VMware, VirtualBox)
- Cybersecurity tools (firewalls, antivirus software)
Utilization of Technology in Computer Information Systems
Computer Information Systems professionals utilize technology to analyze data, design information systems, develop software applications, and manage databases. They rely on tools like:
- Database management systems (MySQL, Oracle)
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software
- Business intelligence tools
- Web development frameworks (React, Angular)
- Project management software (Jira, Trello)
Importance of Staying Updated with the Latest Technologies
Staying updated with the latest technologies is crucial in both IT and Computer Information Systems fields as technology rapidly evolves. Professionals need to continuously upskill to remain competitive and relevant in the industry. By staying abreast of the latest trends, tools, and technologies, individuals can enhance their problem-solving abilities, improve efficiency, and adapt to the changing demands of the digital landscape.
Business Applications
IT solutions play a crucial role in modern business environments, helping organizations operate more efficiently and effectively. Computer Information Systems are utilized to streamline various business processes, leading to increased productivity and improved decision-making.
Implementation of IT Solutions in Business Environments
IT solutions are implemented in business environments through the integration of software applications, hardware systems, and network infrastructure. These solutions help organizations automate tasks, improve communication, and enhance data management. For example, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are used to track customer interactions and improve customer service.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate various business functions to streamline operations and increase efficiency.
Examples of Computer Information Systems in Business Processes
- Supply Chain Management systems are used to optimize the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers.
- Business Intelligence tools analyze data to provide insights for better decision-making.
- Financial Management Systems help organizations manage their finances, budgets, and expenses effectively.
Impact on Organizational Efficiency and Productivity
The integration of IT and Computer Information Systems in business processes has a significant impact on organizational efficiency and productivity. By automating repetitive tasks, reducing manual errors, and providing real-time data analysis, businesses can operate more smoothly and make informed decisions quickly.
This results in improved customer satisfaction, cost savings, and overall competitive advantage in the market.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the exploration of Key Differences Between IT and Computer Information Systems not only highlights their distinct characteristics but also underscores the significance of these disciplines in driving innovation and efficiency across various sectors. By recognizing the nuances between IT and Computer Information Systems, individuals can make informed decisions and leverage the strengths of each field to achieve their professional aspirations.
Detailed FAQs
What are the main differences between IT and Computer Information Systems?
The main difference lies in their focus - IT deals with the implementation and maintenance of technology systems, while Computer Information Systems focus on how technology can support businesses strategically.
What technical skills are required for a career in IT versus Computer Information Systems?
IT professionals need skills in network security, database management, and software development, whereas Computer Information Systems professionals require skills in data analysis, system design, and information management.
How do job prospects differ between IT and Computer Information Systems?
IT offers a wide range of career paths in areas like cybersecurity, cloud computing, and data analytics, while Computer Information Systems roles focus more on optimizing business processes through technology solutions.